What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of cyber attack where attackers create fake websites that look like legitimate ones to steal your personal information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other sensitive data.
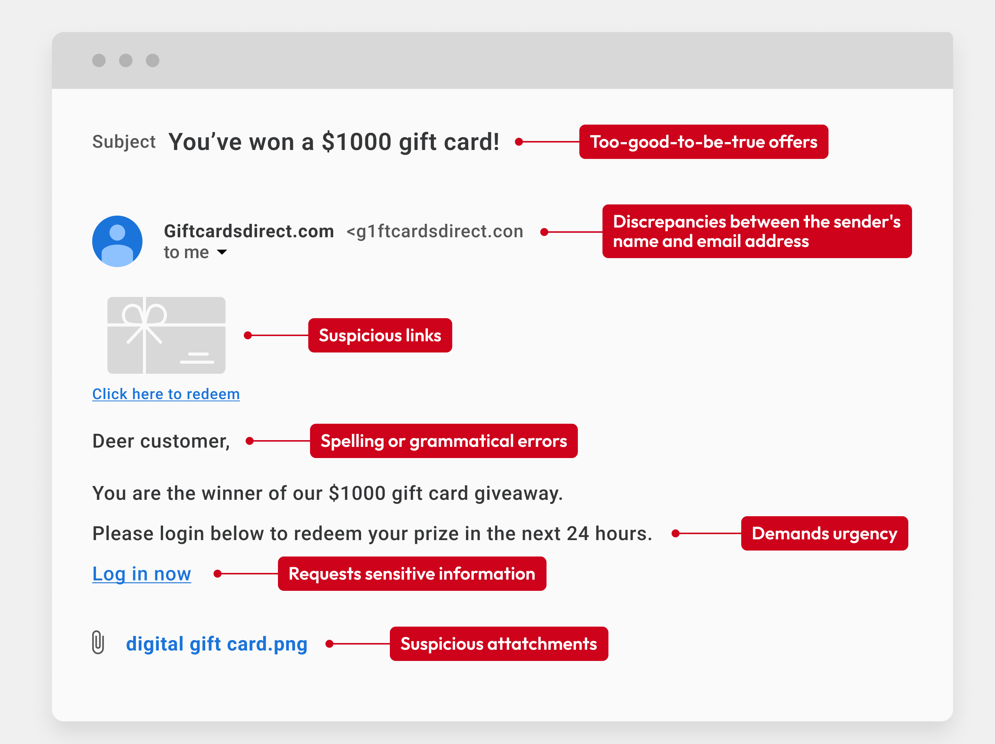
Key Signs of Phishing Websites
1. Check the URL
The most reliable way to identify a phishing website is by carefully examining the URL (web address) in your browser's address bar:
- Look for misspellings or extra characters (e.g., 'amaz0n.com', 'paypa1.com', 'facebook-login.com')
- Check for subdomains that try to trick you (e.g., 'amazon.fake-site.com' - here 'fake-site.com' is the actual domain, not Amazon)
- Be wary of URLs that use numbers instead of letters or contain random strings of characters
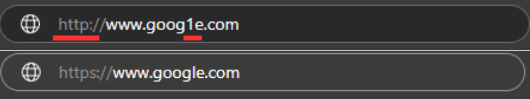
2. Look for HTTPS and the Padlock Icon
Legitimate websites typically use secure connections (HTTPS). In your browser, you'll see a padlock icon next to the URL:
- The absence of HTTPS (just HTTP) should be a warning sign, especially for banking or shopping sites
- Note: Some phishing sites now use HTTPS too, so this alone isn't enough to verify a site

3. Check for Poor Design and Content
Phishing websites often have quality issues that legitimate sites wouldn't have:
- Look for poor grammar, spelling mistakes, or awkward phrasing
- Distorted or low-quality logos and images
- Inconsistent design elements or fonts
- Missing content or features that would normally be present on the legitimate site
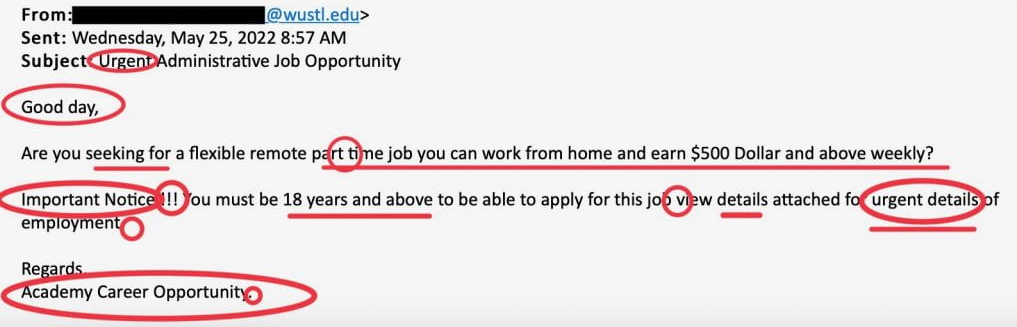
4. Be Suspicious of Urgent Requests
Phishing attacks often create a false sense of urgency to make you act quickly without thinking:
- Messages claiming your account will be suspended unless you "verify" your information immediately
- Alerts about suspicious activity that require your immediate action
- Limited-time offers that seem too good to be true
Practical Protection Steps
1. Verify Site Identity
For important websites (banking, shopping, social media), take these extra steps:
- Bookmark official websites and use these bookmarks instead of clicking on links
- Click the padlock icon in your browser to view the site's security certificate
- Use PhishDetectX to analyze suspicious URLs before visiting them
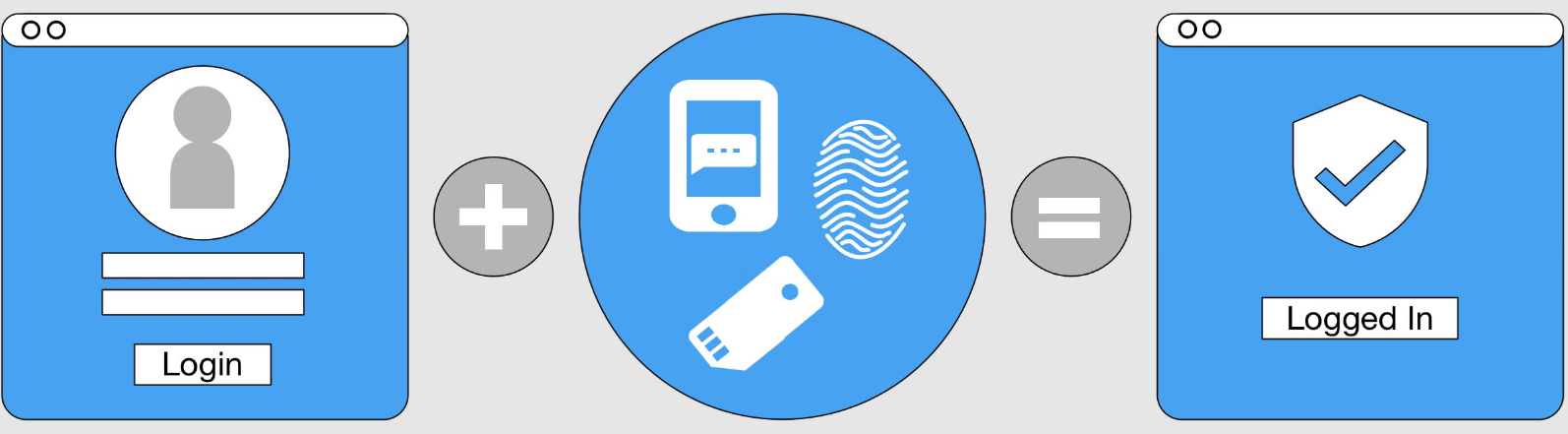
2. Protect Your Accounts
Add extra security measures to your important accounts:
- Use strong, unique passwords for each website
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) whenever possible
- Use a password manager, which will not auto-fill credentials on incorrect domains

3. Be Careful with Emails and Messages
Many phishing attacks start with a link in an email or message:
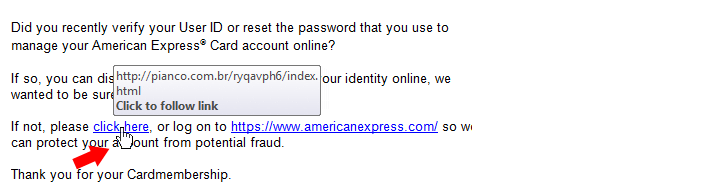
- Hover over links to see the actual URL before clicking
- Be suspicious of emails asking for personal information, even if they appear to be from a trusted organization
- Check the sender's email address carefully - legitimate companies use their own domain (e.g., support@amazon.com, not amazon-support@gmail.com)
4. Watch for Data Entry Forms
Be extra cautious when a website asks for sensitive information:
- Never enter passwords, credit card details, or personal information on a site you accessed via an email link
- Be suspicious if a site asks for more information than necessary
- Check if the form is submitted securely (look for HTTPS in the address bar)
Common Phishing Scenarios
Banking and Financial Phishing
These attempts impersonate banks or financial institutions to steal credentials and financial information:
- Messages claiming there's a problem with your account that needs immediate attention
- Emails about suspicious transactions that you need to verify
- Remember: Banks will never ask for your full password, PIN, or security codes via email or phone
Payment and Shipping Scams
These phishing attempts target customers of popular shopping or delivery services:
- Fake shipping notifications claiming a problem with package delivery
- Emails about suspicious charges asking you to verify your payment details
- Messages about orders you never placed
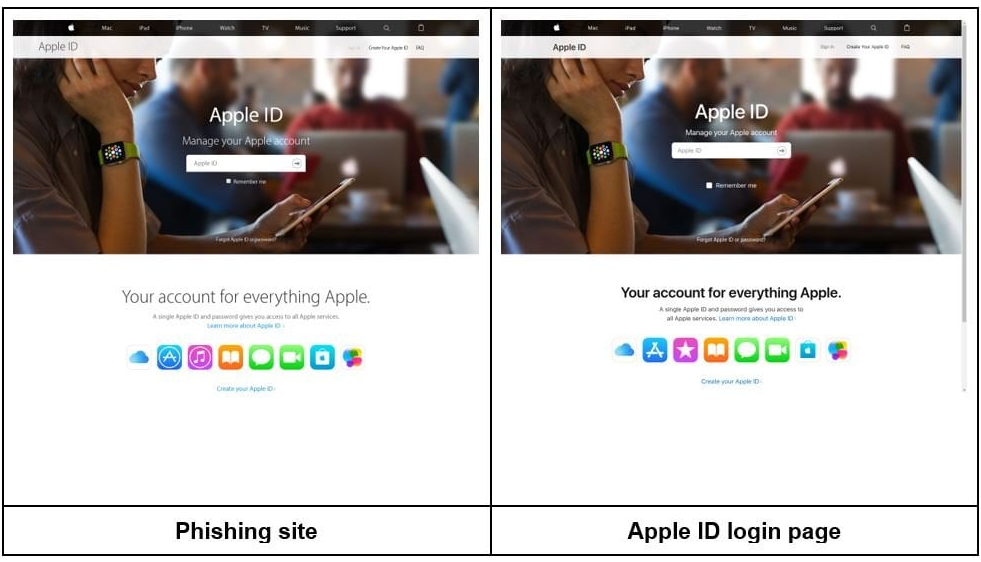
Social Media and Account Takeover
These attacks attempt to gain access to your social media or email accounts:
- Fake login pages for social media platforms
- Messages claiming your account will be suspended unless you "verify" your information
- Notifications about suspicious login attempts that require you to reset your password via a malicious link
What to Do If You Suspect Phishing
If you suspect you're on a phishing site, close the tab immediately. Don't click any buttons, don't fill out any forms, and don't download any files.
If you're concerned about an account, manually type the official website address in your browser (or use a bookmark) and check your account directly.
If you entered any information on a suspected phishing site, change your passwords immediately for all affected accounts. Start with your email and financial accounts.
Report phishing websites and emails to help protect others:
- Forward phishing emails to phishing@nccic.gov
- Report to the Anti-Phishing Working Group at reportphishing@apwg.org
- Report to the organization being impersonated (most have a dedicated email address for this)
Keep a close eye on your accounts for any suspicious activity in the days and weeks following a potential phishing encounter.
Using PhishDetectX to Verify URLs
PhishDetectX is designed to help you identify phishing websites before you visit them:
When you receive a link you're unsure about, don't click it. Instead, copy the URL by right-clicking the link and selecting "Copy link address".
Go to PhishDetectX's homepage, paste the URL into the input field, and click "Check URL".
PhishDetectX will analyze the URL using both machine learning and content analysis to determine if it's likely to be a phishing site.
If either analysis shows a high risk score, treat the site with caution and avoid entering any personal information.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, but by following the guidelines in this guide and using tools like PhishDetectX, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to these scams.
Remember the key warning signs: suspicious URLs, poor quality content, urgent requests, and requests for sensitive information. When in doubt, verify through official channels and use PhishDetectX to analyze suspicious links.